

Next: Knowledge Representation
Up: Compositional Model Repositories
Previous: Compositional Model Repositories
Background: assumption based truth maintenance
An ATMS is a mechanism that keeps track of how each piece of inferred
information depends on presumed information and facts and of how
inconsistencies arise. In an ATMS, each piece of information used or
derived by the problem solver is stored as a node. Certain
pieces of information are not known to be true and cannot be inferred
from other pieces of information, yet plausible inference may be drawn
from them. Such nodes are categorised by a special type and referred
to as assumptions.
Inferences between pieces of information are maintained within the
ATMS as dependencies between the corresponding nodes. In its extended
form (see [8]; or [18]), the ATMS can
take inferences, called justifications of the form
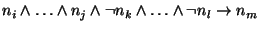 , where
, where
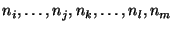 are
nodes that the problem solver is interested in. An ATMS can also take
a specific type of justification, called nogood, that leads to
an inconsistency, of the form
are
nodes that the problem solver is interested in. An ATMS can also take
a specific type of justification, called nogood, that leads to
an inconsistency, of the form
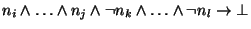 (meaning that at least
one of the statements in
(meaning that at least
one of the statements in
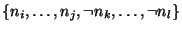 must be false). In the ATMS, these nogoods are represented as
justifications of a special node, called the nogood node.
must be false). In the ATMS, these nogoods are represented as
justifications of a special node, called the nogood node.
Based on the given justifications and nogoods, the ATMS computes a
label for each (non-assumption) node. A label is a set of
environments and an environment is a set of assumptions. In
particular, an environment 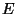 depicts a possible world where all the
assumptions in
depicts a possible world where all the
assumptions in 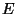 are true. Thus, the label
are true. Thus, the label
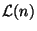 of a node
of a node
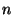 describes all possible worlds in which
describes all possible worlds in which 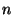 can be true. The label
computation algorithm of the ATMS guarantees that each label is:
can be true. The label
computation algorithm of the ATMS guarantees that each label is:
- Sound - All assumptions in any environment within the
label of a node being true is a sufficient condition to derive that
node:
- Consistent - No environment in the label of a node, other
than the nogood node, describes an impossible world:
- Minimal - The label does not contain possible worlds that
are less general than one of the other possible worlds it contains
(i.e. environments that are supersets of other environments in the
label):
- Complete - The label of each node, other than the nogood
node, describes all possible worlds in which that node can be
inferred:


Next: Knowledge Representation
Up: Compositional Model Repositories
Previous: Compositional Model Repositories
Jeroen Keppens
2004-03-01
![]() , where
, where
![]() are
nodes that the problem solver is interested in. An ATMS can also take
a specific type of justification, called nogood, that leads to
an inconsistency, of the form
are
nodes that the problem solver is interested in. An ATMS can also take
a specific type of justification, called nogood, that leads to
an inconsistency, of the form
![]() (meaning that at least
one of the statements in
(meaning that at least
one of the statements in
![]() must be false). In the ATMS, these nogoods are represented as
justifications of a special node, called the nogood node.
must be false). In the ATMS, these nogoods are represented as
justifications of a special node, called the nogood node.
![]() depicts a possible world where all the
assumptions in
depicts a possible world where all the
assumptions in ![]() are true. Thus, the label
are true. Thus, the label
![]() of a node
of a node
![]() describes all possible worlds in which
describes all possible worlds in which ![]() can be true. The label
computation algorithm of the ATMS guarantees that each label is:
can be true. The label
computation algorithm of the ATMS guarantees that each label is:
![\begin{displaymath}\begin{split}\forall E,&[(\wedge_{n_i\in E}n_i) \wedge (\wedg...
... \wedge (\wedge_{\neg n_i\in E'}\neg n_i) \vdash n] \end{split}\end{displaymath}](img252.gif)