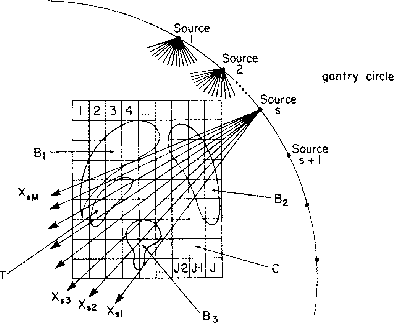
Figure 6: Radiotherapy treatment planning (from [Censor et al. 1988])

Figure 6: Radiotherapy treatment planning (from [Censor et al.
1988])
Radiation therapy is a widely-used method of treating tumors [Censor et al. 1988]. A linear accelerator which produces a radioactive beam is mounted on a rotating gantry, and the patient is placed so that the tumor is at the center of the beam's rotation. Depending on the exact equipment being used, the beam can be shaped in various ways as it rotates around the patient. A radiotherapy treatment plan specifies the beam's shape and intensity at a fixed number of source angles.
A map of the relevant part of the patient's body, with the tumor and all important structures labelled, is available. Also known are good clinical forward models for calculating, from a treatment plan, the distribution of radiation that will be delivered to the patient's tissues. The optimization problem, then, is to produce a treatment plan which meets target radiation doses for the tumor while minimizing damage to sensitive nearby structures.
The current practice is to use simulated annealing for this problem. We will apply the methods of Sections 3 and 4 to learn to improve the performance of simulated annealing over a distribution of problem instances (maps of tumors and surrounding structures). We have also investigated a linear-programming solution to a modified formulation of this problem. The methods of Section 4 may be applicable for optimizing the parameters of the linear program, as well.