Windows Operating System
This page is an introduction to the Windows Operating System and
the skills that you will need to use it for programming. Other Microsoft
operating systems (Windows NT, XP, 95/98, Millenium, etc.) operate similarly.
At the beginning of the course, when we are just starting to learn programming,
practice these skills repeatedly, until they become intuitive. Because
there are just a few skills, and because you will use these same skills
over and over again while taking this course, you will soon master them.
The Windows 2000/NT Operating System
Windows 2000 is built on the older, more well known Windows NT Operating
system (OS). Both are a 32 bit, multitasking OS. Version 1.0 of Windows
NT was released in 1994. Its initial size was 6 millions lines of code,
which cost Microsoft $150 million. Windows 2000 (the successor to Windows
NT) is estimated to contains 50 million lines of code.
Windows Terminology
Here are a few important terms that you must know to be able to understand
the rest of the information on this page.
Desktop
The entire screen, which contains the Task Bar, Icons,
and Windows.
Task Bar
The horizontal bar that appears at the bottom of the Destktop.
It always contains the Start Button and buttons for any minimized
applications.
Start Button
The button that appears on the left of the Task Bar.

Icons
Pictures with names underneath: e.g., My Computer which is typically
in the upper left hand corner of the Screen. Icons represent applications
(that you can run) files (data for applications that you can run) or Folders
(repositories for files that you can examine) by Double Clicking.

Clicking
Pressing and quickly releasing a mouse button. Typically refers to
the left button: a longer way to say this is Left Clicking
(most mouses also contain a right button).
Right Clicking
Pressing and quickly releasing the right mouse button.
Double Clicking
Clicking twice, in rapid succession. Typically refers to the
left
button. This takes a bit of practice for beginners.
Dragging
Pressing the mouse button and moving the mouse while the button is
pressed.
Folders
Manila folder Icons. Folders organize data: applicatons, files
and [sub]folders. Double Clicking a folder shows its contents (the
applications, files, and subfolders that it contains).

Window
A Window shows a running application and the data it is working on.
Double
Clicking an application or a file (connected to an application) starts
the application (working on the data in the file), creating a window.
Window Control
A control on the top right part of a Window that affects its
size.
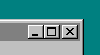
-
_ Minimize: Show window only on the Task Bar
-
[_] Maximize/Mimimize: Window fills Desktop
or restores to previous size
-
X (Terminate): discard the window
If a window is minimized, click it on the task bar and it will open
and move to the desktop. When a window on the desktop is maximized, it
fills the entire screen; when such a screen-filling window is midimized,
it returns to its original desktop size.
If a window is minimized, click it on the Dock and it will open
and move to the Desktop. When a window on the Desktop is
maximized, it fills the entire screen; when such a screen-filling window
is midimized, it returns to its original Desktop size.
Explorer
A application running in a Window that is used to explore/manipulate
files and folders. The easiest way to start an Explorer is by Right
Clicking the Start button and then Clicking Explore.
Context Menu
Right Clicking on Windows, buttons, or Icons brings
up a small window containing a list of operations; the user can select
which operation (from the list) to perform by clicking it.
Miscellaneous Operations
Renaming Folders and Files
To rename a folder or file (if it is a file with an extension,
the extension should remain the same: you will be warned if you accidentally
change it);
-
Right Click the folder or file.
-
In its context menu, click the Rename option.
-
Type the new name (and the same extension) in the highlighted blue box.
The folder or file should now have the name that you typed.
Enabling Scrolling in the Java Console
Window
Java programs often input/output text in the console window.
If scrolling is enabled on these windows, you can look at all the text
printed. On some Windows operating systems (e.g., Windows 2000), this is
the default (300 lines); on others (e.g., Windows NT) you must follow the
instructions below. To allow [more] scrolling in this window, so that you
can see a [longer] history of all your program's input/output, perform
the following steps (you may have to perform these steps each time that
you log on):
-
Right Click in the header (on the top of the frame) of the Console Window.
-
Click Properties.
-
Select the Layout tab.
-
In the Screen Buffer Size section, type 1000 (or an even bigger
number) into the Height text field.
-
Click OK.
-
On the Apply Properties window, check the bullet marked Save
properties for future windows with same title.
-
Click OK.
The console window should now be scrollable (you should see the scrolling
tab along the right border of the window)
Viewing File Extensions
File extensions are the the part of the file name after the
period (e.g., the mcp in project.mcp or the java in
Application.java). It is often very useful to be able to see both
file names and extensions. On some Windows operating systems (e.g., 2000),
this is the default; on others (e.g., NT) you must follow the instructions
below.
-
Open an Exlorer window.
-
Select View | Options...
-
Click the View tab, if it is not already visible.
-
Ensure the box labeled Hide file extensions for known types is NOT
checked (click it if it is checked to toggle it to unchecked).
-
Click OK
You should now be able to see the extensions of all files.
Using Windows Machines in Campus
Clusters
Logging On
The following instructions are for logging onto any machine
running Windows 2000 in CMU's Clusters; these include WeH 5204 (40 machines),
WeH 5205 (12 machines), Cyert 100 (25 machines), and Baker 140 CEF (70
machines). You can do coursework from machines in any of these clusters.
-
Hold down the Ctrl and Alt keys and press the Del
key (often written Ctrl+Alt+Delete); a Log on to Windows
box will pop up.
-
In the User Name box, enter your Andrew username.
-
In the Password box, enter your Andrew password (it will appear
a *s).
-
Ensure the Log on to option box says ANDREW.CMU.EDU (Kerberos
Realm); if it is showing anything else, select this option from this
option box.
-
Click the icon labelled Log In or press the Enter/Return
key.
If you enter your username and password correctly, you will be logged on;
otherwise repeat this process until you successfully logged on.
Logging Off
When you are finished working on a cluster machine, you should
always log off. Before logging off, make sure to backup (via Andrew) all
your files that contain useful information. Then ...
-
Drag and Drop all your folders/files from the desktop into the Recycle
Bin icon.
-
Drag and Drop all your folders/files from c:\temp into the
Recycle
Bin icon.
-
Double Click the Recycle Bin icon.
-
Select File | Empty Recycle Bin.
-
Click Yes for Confirm multiple File Delete.
To actually log off
-
Click Start and select Shutdown....
-
The What do you want the computer to do text field should show Log
off username (where username is your username
on Andrew); if this action is not selected, select it.
-
Click OK or press Enter/Return.
At this point the machine will begin logging you off. To ensure
that this operation is successful, you should wait until the Welcome
to Windows box displayed.
