8. Debugging and the Inspector
Amulet contains many features to aide in debugging programs. Many of these are available interactively through the ``Inspector''. Other features are available programmatically. This chapter provides a reference manual for the Inspector and the other debugging facilities, and concludes with a set of recommendations about how to debug various situations that we have seen frequently.
We want to make Amulet programs very easy to develop and debug. Therefore, we have added extensive error checking to Amulet, as well as a number of interactive and tracing tools. These are designed to work with your regular C++ debugging tools like breakpoints. For example, the Inspector will allow you to break into the debugger when a slot is set, but then you need to use your regular C++ debugger to figure out why the slot was set. The debugging features are all implemented using machine-independent code, except for a single routine that breaks into the debugger. Therefore, we assume you can do stack traces and look at variables in your debugger, rather than needing to do this in our tools.
We would very much like to enhance the debugging capabilities of Amulet. If you think of a facility that would be useful, please let us know. An article about the debugging facilities in Amulet is available from the Amulet web site.
The interactive Inspector is included by default in the Amulet library when you build the debugging option (see Section 8.4 of the Overview document). To use the Inspector, if you have the debugging library, you do not need to do anything special in your application. However, if you want to use any of the debugging features procedurally, you must include the debugger.h file, because it is not included by default when you include amulet.h. The most portable way to include the debugger header file is:
#include <am_inc.h>
#include DEBUGGER__H
8.3 Inspector
The Inspector is an interactive program that provides access to a large number of debugging features. At its most basic, it displays the slots of an object in a window. The values of most types of slots can be edited. The properties of the slots and the object can be inspected, as well as dependencies of any formulas in the slots. Traces and breakpoints can be set when slots are accessed or set. The Interactor's tracing mechanisms are also available from the Inspector.
To pop up the Inspector on an object, you can put the cursor over the object, and hit the F1 key (see Section 8.3.1.1 about how to change the keys, if necessary). The inspector will first print out the window and location in the window of the cursor to the transcript (console) window, and then a new top-level window will appear displaying all the slots of the object and their current values. If no object is under the cursor, then the window itself will be inspected. The Inspector first tries to find a primitve (leaf) object under the cursor, but if that fails, then it presents the front-most group object. If the correct object does not appear, it is usually best to get to the object by going up and down the owner/part tree, as will be explained below.
If you press the F2 key over an object, the Inspector will do the same search for an object, but will only print out the position in the window and the object at that position. This is also very useful for finding out the coordinates of a point in the window.
The F3 key will ask in the console window for the name of an object to inspect. The name typed must be the exact name of the object, which is sometimes an easy-to-remember constant name (like Amulet's or the user's prototypes) or often cut and pasted from the output of one of the tracing functions.
The inspector can also be invoked procedurally using either of the functions:
// inspect the specific object
void Am_Inspect(Am_Object object);
// The next one takes the name of the object. This is useful from an interpreter.
void Am_Inspect(const char * name);
8.3.1.1 Changing the Keys
If you want to use F1, F2, and F3 for your own functions, you can always eliminate all of debugging facilities, including the inspector, by building a non-debug version of the library (see the Overview Chapter).
If you want to bind the editing functions to different keys, you can use the function:
extern void Am_Set_Inspector_Keys(Am_Input_Char show_key,
Am_Input_Char show_position_key,
Am_Input_Char ask_key);
which is exported from debugger.h. This function takes an Am_Input_Char, but a string will also work. Passing in the null character to any of these, by using Am_Input_Char(), will mean that that function is not available. The first parameter controls the normal popping up of the Inspector (normally bound to F1), the second parameter is for just printing the object under the mouse (normally F2), and the third is to prompt from the keyboard (normally F3). The test program testinter has a test of rebinding the Inspector's keys using this function.
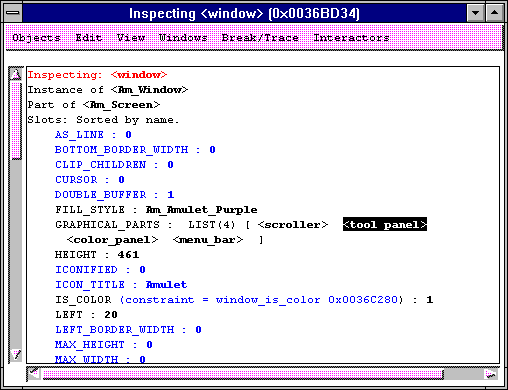
The inspector window is shown above. All of the slots of the objects are shown along with their current values. Inherited slots are shown in blue, and local slots are shown in black. You can click on a slot value to show a cursor, and then the value can be edited.
You can double-click on a slot name, an object name, or a constraint name to select it, and then perform other operations on that slot, object or constraint (such as viewing its properties). For the commands which pop-up windows, you can select names in those windows as well by double-clicking on them. The name which is selected by double-clicking is also copied into the cut buffer (clipboard) so it can be pasted into this or other applications.
Also shown in the Inspector window, below the list of slots (in this case, you would need to scroll down using the scroll bar on the left) is (optionally) a list of the parts of the object, and the instances of the object.
Commands available from the menus are (many of these are described in detail below):
- Objects: This menu contains commands that operate on objects, and also the ``Done'' commands (that would normally be in a ``File'' menu). Commands in this menu are:
- Inspect Object: If an object is selected (by double-clicking with the left button on an object name), then this command inspects that object in this window. Accelerator for this is ^i (for ``Inspect''), but you can also point at an object name with the right button, without even selecting the name first.
- Inspect in New Window: If an object name is selected, then this will cause it to be inspected in a new window. Accelerators are ^-shift-I, or pointing at the object name using SHIFT-right-button.
- Inspect Object Named...: This pops up a dialog box into which you can type an object name. If the name has been put into the window manager's clipboard (using cut or copy, or equivalent), then you can paste the name using the middle mouse button or ^y (for ``yank''). The new object is inspected in the same window.
- Inspect Previous: Shows the previous object shown in this window again. There is a stack of all the objects shown in each inspector window, and this effectively does a ``pop''. Accelerator is ^p.
- Refresh: Most of the time, the inspector window will correctly refresh to show the current values of the object. Sometimes, however (especially if you turn off Automatic Refresh) the display will not correctly show the state of the object, in which case you should use the Refresh command to get the current values of all of the slots.
- Flash Object: If an object is selected (by double-clicking on its name), then this will cause the object's window to come to the front, and the object to flash. If the object is not visible for some reason, then this prints an explanation of why not to the console window (eventually, we will print it to a dialog box). Thus, this command is useful for seeing where objects are, or why they might not be visible. If no object is selected, then this command operates on the current object being inspected. Accelerator is ^f.
- Done: This gets rid of the current inspector window. Accelerator is ^q (for quit). You can also use the regular window manager mechanism for getting rid of windows, like ``Kill Window'' under Motif, or the ``Close'' command under Windows NT.
- Done All: This gets rid of all inspector windows.
- Quit Application: This kills the application and all the inspector windows. This does not ask for confirmation, and it does not notify the application or try to recover gracefully, it just exits the main event loop.
- Edit: This menu will eventually contain all the commands to edit the values of slots. For now, it only has one sub-command:
- View: This menu contains various commands for specifying what is viewed in the main window, and how. Most of the sub-commands are toggles, and switch between two labels.
- Hide Inherited Slots / Show Inherited Slots: By default the inherited and local slots are all shown. This command will toggle whether the inherited slots are shown at all.
- Hide Internal Slots / Show Internal Slots: By default, the internal and normal slots of the object are all shown. By convention, the internal slots are those whose names begin with a tilde (~). There is no system-defined enforcement of internal vs. regular slots currently. It is generally a bad idea to change the values of internal slots. This toggles whether the internal slots are shown.
- Show Parts / Hide Parts: By default, all of the parts of an object are shown below the list of the slot names (you may need to scroll down). This command toggles whether the parts are shown.
- Show Instances / Hide Instances: By default, the instances of the object are not shown. This command will toggle whether all the instances of the object are shown below the list of parts at the bottom of the window (you may need to scroll down).
- Automatic Refresh / Manual Refresh: By default, whenever a value in the inspected object changes, the display is refreshed to always show the current value (note that this is not guaranteed; it is best to use the Refresh command if you want to guarantee the values are up-to-date). However, updating the inspector may substantially slow down the execution of your program. Therefore, you might want to toggle to Manual Refresh, which means that the inspector window will not be updated until you explicitly call the Refresh command (in the Object menu).
- Show Old Slot Values: This is an experimental feature that displays the old values of the slot, as well as the current value. It only works for some types of values, and there is currently no way to get rid of the display except to get rid of the inspector window. Let us know if you find this feature useful, and we may make it more robust.
- Sort by Name / Stop sorting by Name: By default, the display of the slots is sorted by the slot name in alphabetical order. This toggle will cause the slots to instead be shown in the order they appear in the object, which is somewhat faster.
- Windows: This menu contains commands that pop up property windows that give more information about the selected object, slot or constraint. If you select a different object, slot or constraint, the pop-up window will move and show the properties of that one instead. You can get rid of these pop-up windows using the regular window manager mechanism (such as the close box or Kill Window window-manager command). Just like in the main Inspector window, you can double-click on objects, slots and constraints listed in these pop-up windows to select them (or right-button clicking for objects). However, you cannot change (edit) any values in the pop-up windows.
- Show Prototypes and Owners: If an object name is selected, then this pops up a window that shows the object's name, its prototype's name, and that object's prototype, etc. all the way up to the root object. Similarly, it also shows the owners all the way up to the screen (or to an object with no owner for objects that are not on the screen). If no object name is selected, then this operates on the object being inspected.
- Show Constraint Dependencies: If the name of a formula is selected, then this pops up a window that shows the slots that the formula is currently depending on, and the current values of those slots. If those slots also contain a formula, then the dependencies of those are shown also, down to a depth of three. You can always double-click on a constraint in this window, to see its dependencies.
- Show Slot Properties: If a slot name is selected, then this pops up a window that displays a number of properties of the slot. Most of these are the advanced properties such as declarations for inheritance and the demon bits. The most useful non-advanced properties are that for inherited slots, it shows the object from where the slot is being inherited from (which will be somewhere up the prototype chain), and the current type of the value in the slot.
- Show Slot Uses: If a slot name is selected, then pops up a window that shows all the formulas which use this slot. This will show you what will be affected if the slot value changes.
- Break/Trace: This menu contains commands that allow breaks and traces to be set on slot setting, either by direct setting or by constraints being re-evaluated. ``Traces'' print to the console, and ``breaks'' cause your C++ debugger to be entered (so you should be running the application in the debugger before using breaks).
- Interactors: This menu provides access to the various Interactor tracing facilities described in Section 5.7 of the Interactors chapter. All of these output to the console window.
8.3.3 Viewing and Editing Slot Values
When you inspect an object, the values of the slots are displayed. You can control which slots are viewed, by hiding or showing the inherited slots and/or the internal slots. You can also control the sorting of the slots (either alphabetical or in the order they appear in the object).
If you single click with the left mouse button over a slot value, a cursor will appear and you can edit the slot's value. The editing keys are the same as for all other text interactors (Section 5.3.5.5.1 of the Interactors chapter). Currently, the inspector will not let you change the type of the value in the slot. Therefore, it uses the current type of the value to decide how to parse the input value. You can edit primitive values, like integers, floats and strings. Depending on whether your compiler supports bools as a primitive type, they will either print out as true and false or 1 and 0. Floating point values print out just like integers if there is no fraction part. You can use the slot properties pop-up window to find out the exact slot type.
For slots which contain named values, like styles (Am_Red, Am_Line_8), objects (Am_Rectangle_123), constraint names (windows_is_color) and method names (rectangle_draw), you can type in a new name. Amulet remembers the names of all built-in or user-defined objects, methods and formulas. If you create your own styles or wrappers, you can arrange for them to have names registered in the database using the ``registry'' mechanism defined in registry.h. For any wrapper object, you can register its name using the Am_Register_Name procedure, such as:
Am_Register_Name (my_color_object, "my_color");
Then, the user will be able to type in my_color as the value of a slot.
Unfortunately, you cannot yet set the value of slots that are Am_Value_Lists, and you cannot set the items of an Am_Value_List.
Sometimes it might be useful to access the debugging functions from a program, instead of interactively from the Inspector. For example, you program might be crashing even before it fully starts up, so you cannot access the inspector. If you program gets past the Am_Initialize(), then you can still trace slot setting and print the values of the slots of objects. Also, some of these procedures might be executed from a debugger such as gdb that supports calling functions.
The functions for invoking the Inspector procedurally have already been listed:
// inspect the specific object
void Am_Inspect(Am_Object object);
// The next one takes the name of the object. This is useful from an interpreter.
void Am_Inspect(const char * name);
You can cause an object to be ``flashed'' so you can see where it is on the screen. If it is not visible, then this functions writes the reason to the specified stream:
void Am_Flash (Am_Object o, ostream &flashout = cout);
The tracing functions provide significantly more features than are available interactively from the inspector. The tracing and breaking function takes an optional object, an optional slot, and an optional value. Whatever ones of these are supplied will control whether to trace or break. Thus, if only the object is supplied, then the trace or break will happen whenever any of the slots of that object are set. If only a value is supplied, then a trace or break will happen whenever any slot of any object is set to that value. If all three parameters are supplied, then a trace or break will happen only when that slot of that object is set to that value.
void Am_Notify_On_Slot_Set (Am_Object object = Am_No_Object,
Am_Slot_Key key = 0,
Am_Value value = Am_No_Value);
void Am_Break_On_Slot_Set (Am_Object object = Am_No_Object,
Am_Slot_Key key = 0,
Am_Value value = Am_No_Value);
The next procedure clears a slot notify or break set with the above procedures:
void Am_Clear_Slot_Notify (Am_Object object = Am_No_Object,
Am_Slot_Key key = 0,
Am_Value value = Am_No_Value);
8.5 Hints on Debugging
This section lists some hints of procedures we have found useful for debugging certain situations that we have found occur more than once. If you know anything that should be added to this list, please let us know!
- I click on an object but nothing happens: If you think that an interactor should be running, but it doesn't, it is usually very helpful to turn on Interactor tracing from the Inspector, and see what interactors are running, and what slots they are setting. Although this often prints out a tremendous amount of information, and significantly slows down execution, it is usually worth it. Typical reasons that Interactor's don't seem to execute include:
- My Interactor is modifying the group itself instead of the members of the group, or affecting the members of a group, and I want it to affect the group itself: The default
Am_START_WHERE_TEST of Interactors tries to be smart about which object to affect, based on the type of the object the Interactor is attached to. You can specifically tell the Interactor which to affect by setting the Am_START_WHERE_TEST slot to one of the built-in functions (such as Am_Inter_In or Am_Inter_In_Part) or to a custom function.
- The slot has the wrong value: There are various reasons this might happen:
- I want to set a widget to have a certain value, but it isn't working: To set the value of a widget, you have to set the
Am_VALUE slot of the widget itself. Although the Am_VALUE slot of the command object usually provides the same value, it does not affect the widget to set this slot in the command object. For button-type widgets, the value should either be NULL, or the label or ID of the particular item to become the value (based on the value of the Am_LABEL slot or Am_ID slot of the command object for that item).
- I set the value of a button, or click on it, but I can't see the value: By default, buttons do not stay ``indented'' when they are pressed. If you want a button to show the value, you have to set its
Am_FINAL_FEEDBACK_WANTED slot to true.
- My constraint is crashing or calculating the wrong value: Because constraints are normal C++ code, you can used your debugger to set breakboints in the constraint code to see why it is calculating its current value. Also, in the Inspector, you can select the slot the constraint is in and set a trace or break on the slot to see when the slot is changing value.
- My application crashes at start up: Usually this is caused by constraints calculating incorrect values. Amulet supports ``Uninitialized'' values for constraints, but sometimes this is not sufficient to allow constraints to work. You probably need to put a few
obj.Valid() tests, or instead of getting a slot value directly into a variable, use an intermediate Am_Value. For example:
i = 3 / (int)obj.GV(SLOT); //crashes because returns 0 when not initialized
Am_Value v;
obj.GVM(SLOT, v); //remember to change macro to be GVM
if (v.Valid()) {
i = 3 / (int)v;
- The constraint in my slot disappeared: Remember that constraints go away by default when the slot is set, so if an interactor or your program sets the slot, the constraint will be removed. You can see when the slot value is set by setting a break or trace on slot setting using the Inspector. To make sure the constraint is retained, you can set single-constraint-mode to be false for the slot. See Section 3.11.5 of the Ore chapter.
obj.Set_Single_Constraint_Mode(SLOT,false);
- The constraint is not being re-evaluated when it should be: Usually, this is because there isn't a dependency where there should be. Make sure that the references in the formula use
GV or GVM and not Get or else no dependency will be established. You can select the constraint in the Inspector and check its dependencies. Also, it might be useful to trace or break when the slot's value changes and when the depended on slot's value changes, to make sure that they are really changing.
Last Modified: 03:34pm EDT, May 24, 1996

