

Next: aDCSP + preferences =
Up: Inference
Previous: Scenario + Knowledge Base
From model space to aDCSP
Once the model space has been constructed, it can be translated into
an aDCSP. The translation procedure, summarised as algorithm
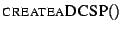 , consists of three steps as described
below:
, consists of three steps as described
below:

- Generate the attributes and domain values from the
assumptions. The aDCSP attributes correspond to the underlying
assumption classes (i.e. groups of assumptions indicating
alternative choices with regards to the same model construction
decision). A relevance assumption and its negation jointly form an
assumption class. For example,
 {(relevant growth
frog),
{(relevant growth
frog),  (relevant growth frog)} specifies such an
assumption class. The set of model assumptions involving the same
participants/relations, but with different model names and hence
different descriptions, also form an assumption class. For
instance,
(relevant growth frog)} specifies such an
assumption class. The set of model assumptions involving the same
participants/relations, but with different model names and hence
different descriptions, also form an assumption class. For
instance, 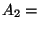 {(model
{(model
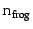 exponential), (model
exponential), (model
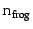 logistic), (model
logistic), (model
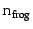 other)},
where
other)},
where
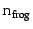 is a variable denoting the size of
a population, specifies such an assumption class. Running this step
of the algorithm, an attribute is created for each assumption class,
with the domain of such an attribute consisting of all assumption
instances in the assumption class.
is a variable denoting the size of
a population, specifies such an assumption class. Running this step
of the algorithm, an attribute is created for each assumption class,
with the domain of such an attribute consisting of all assumption
instances in the assumption class.
- Create activity constraints. The attributes and domain
values generated in the previous step are only meaningful in
situations where the participant and/or relation instances contained
in the arguments of the corresponding assumptions exist. For
example, the assumption (model
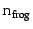 logistic) is only relevant if the participant instance
logistic) is only relevant if the participant instance
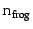 exists. Clearly, all assumptions
within one assumption class have the same participant and/or
relation instances as their arguments. Because each assumption
class corresponds to one attribute, the attribute can be activated
if and only if the participant and/or relation instances associated
with the related assumption class are active. Therefore, this step
creates activity constraints that activate an attribute based on the
conjunction of the environments contained within the labels of the
participants/relations of the assumption class. For instance, as
can be deduced from Figure 7,
exists. Clearly, all assumptions
within one assumption class have the same participant and/or
relation instances as their arguments. Because each assumption
class corresponds to one attribute, the attribute can be activated
if and only if the participant and/or relation instances associated
with the related assumption class are active. Therefore, this step
creates activity constraints that activate an attribute based on the
conjunction of the environments contained within the labels of the
participants/relations of the assumption class. For instance, as
can be deduced from Figure 7,
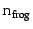 is activated when (relevant
growth frog) is committed. Thus, the attribute corresponding to
assumption class
is activated when (relevant
growth frog) is committed. Thus, the attribute corresponding to
assumption class 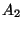 , defined in step 1, is activated under the
attribute value assignment associated with the (relevant
growth frog) assumption.
, defined in step 1, is activated under the
attribute value assignment associated with the (relevant
growth frog) assumption.
- Create compatibility constraints. In the ATMS (or model
space), all sources of inconsistencies are contained in the label of
the nogood node. Therefore, the compatibility constraints are
created directly by translating the environments in the label
 into the corresponding conjunctions of attribute-value
assignments.
into the corresponding conjunctions of attribute-value
assignments.


Next: aDCSP + preferences =
Up: Inference
Previous: Scenario + Knowledge Base
Jeroen Keppens
2004-03-01

