


Next: Computational expenses
Up: Results
Previous: Results
The first goal of this research was to compare the accurracy of Bayesian
learning forecast against other neural network and regression models.
We use Azoff's NN benchmarks [1],
the results of an implementation of backpropagation in MUME [4], the Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines method [3]
and compare them with the results obtained using Neal's implementation of Bayesian learning [7].
Table 1 shows the result for the Mackey Glass series without
noise and Table 2 for the series with 20% of noise added to
the targets.
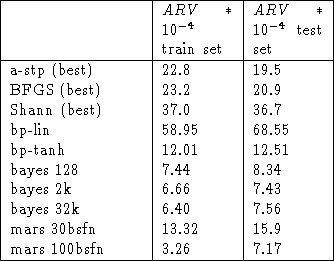
Table 1: Performances in Mackey Glass series.
a-stp: Hertz rules adaptive steepest descent with weight update per
pattern. shann: is the Shanno varian of conjugate gradients with
inexact line search. BFGS: is the quasi-Newton method with inexact line search.
The error ARV is the average relative variance:
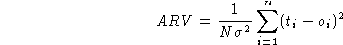
where the  is the standard deviation of each set. The
normalization implies that if the estimated mean of the data is used as
predictor, ARV=1 is obtained.
is the standard deviation of each set. The
normalization implies that if the estimated mean of the data is used as
predictor, ARV=1 is obtained.
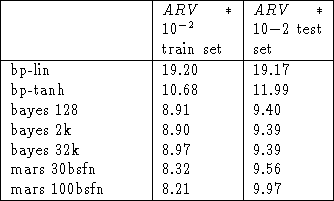
Table 2: Performances in Mackey Glass series with 20% noise in the
targets
In the case of Bayes the mean ARV for 200 Markov Chain Monte Carlo states is
shown.
Rafael A. Calvo
Fri Apr 18 12:26:35 GMT+1000 1997

