Back to "Biological Language Modeling Seminar Topics"
Back to "Protein sequence analysis"
Measures of similarity in amino acid sequences [compare to measures of similarity in protein structures]
* The 20 amino acids have different side-chains with distinct chemical and physical properties, which depend on the local environment.
Because of the chemical structures of the side chains, there is an overlap in these properties:

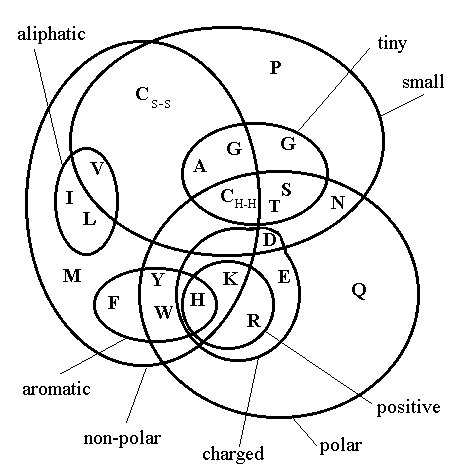
Figure: Venn diagram showing the relationship of the 20 naturally occurring amino acids to a selection of physio-chemical properties thought to be important in the determination of protein structure. Taken on September 30, 2002 from http://prowl.rockefeller.edu/aainfo/pchem.htm
* The extent to which each amino acid exhibits a certain property has been quantified: http://us.expasy.org/cgi-bin/protscale.pl
* Some of these properties include:
Molecular weight Number of codon(s) Bulkiness Polarity / Zimmerman Polarity / Grantham Refractivity Recognition factors Hphob. / Eisenberg et al. Hphob. OMH / Sweet et al. Hphob. / Hopp & Woods Hphob. / Kyte & Doolittle Hphob. / Manavalan et al. Hphob. / Abraham & Leo Hphob. / Black Hphob. / Bull & Breese Hphob. / Fauchere et al. Hphob. / Guy Hphob. / Janin Hphob. / Miyazawa et al. Hphob. / Rao & Argos Hphob. / Roseman Hphob. / Wolfenden et al. Hphob. / Welling & al Hphob. HPLC / Wilson & al Hphob. HPLC / Parker & al Hphob. HPLC pH3.4 / Cowan Hphob. HPLC pH7.5 / Cowan Hphob. / Rf mobility HPLC / HFBA retention HPLC / TFA retention HPLC / retention pH 2.1 HPLC / retention pH 7.4 % buried residues % accessible residues Hphob. / Chothia Hphob. / Rose & al Ratio hetero end/side Average area buried Average flexibility alpha-helix / Chou & Fasman beta-sheet / Chou & Fasman beta-turn / Chou & Fasman alpha-helix / Deleage & Roux beta-sheet / Deleage & Roux beta-turn / Deleage & Roux Coil / Deleage & Roux alpha-helix / Levitt beta-sheet / Levitt beta-turn / Levitt Total beta-strand Antiparallel beta-strand Parallel beta-strand A.A. composition A.A. comp. in SWISS-PROT Relative mutability
These properties have predictive value, e.g. hydrophobicity.
* 256 different scales are quoted in Williams, R.M., Obradovic, Z, Mathura, V., Braun, W., Garner, E.C., Young, J., Takayama, S., Brown, C.J., Dunker, A.K. (2001) "The protein non-folding problem: amino acid determinants of intrinsic order and disorder" Pac. Symp. Biocomp.
* Because of the overlap in properties, amino acids are sometimes replaceable by others in a protein sequence. This forms the basis for similarity searches of biological sequences, that differ from exact matches desired in text matching (for review see Vogt, G., Etzold, T. and Argos, P. (1995) An assessment of amino acid exchange matrices in aligning protein sequences: the twilight zone revisited. J. Mol. Biol. 249, 816-831). There are many different 20x20 exchange tables in use (see Table 4 in this review).
- substitution matrices
PAM http://helix.biology.mcmaster.ca/721/distance/node9.html
PAM/MDM/Dayhoff; BLOSUM, see http://twod.med.harvard.edu/seqanal/submatrix.html
BLOSUM see http://helix.biology.mcmaster.ca/721/distance/node10.html
- amino acid properties
- volume and polarity of amino acid types
- secondary structural properties
- exact residue conservation
- minimum number of base changes per codon
- genetic code distance
- evolutionary model for point mutations
* reduced amino acid alphabets
How many sequences in genomes have sequence homologues?
See figure 5.2 in Chapter 5 Ref_LengauerI