



Next: Markovian arrival process
Up: Quasi-birth-and-death process
Previous: Examples of QBD processes
Contents
In general, a QBD process is a Markov chain on the state space
 , where the state space
can be divided into levels, and level
, where the state space
can be divided into levels, and level  has
has  states
(phases) for each
states
(phases) for each  3.2.
For example, in Figure 3.8(b),
3.2.
For example, in Figure 3.8(b), 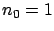 and
and  for
for  .
In a QBD process, transitions are allowed only
to the neighboring levels or within the same level.
Thus, a QBD process has a generator matrix of the form:
.
In a QBD process, transitions are allowed only
to the neighboring levels or within the same level.
Thus, a QBD process has a generator matrix of the form:
 |
(3.2) |
where submatrix
 encodes (forward) transitions from level
(column)
encodes (forward) transitions from level
(column)  to level
to level  for
for  , submatrix
, submatrix
 encodes (backward) transitions from level
encodes (backward) transitions from level  to level
to level  for
for  , and submatrix
, and submatrix
 encodes (local) transitions
within level
encodes (local) transitions
within level  for
for  .
Specifically,
(
.
Specifically,
( ) element of
) element of
 is
the transition rate from state
is
the transition rate from state  , i.e. phase
, i.e. phase  of level
of level  ,
to state
,
to state  for all
for all  ;
(
;
( ) element of
) element of
 is
the transition rate from state
is
the transition rate from state  to state
to state  for all
for all  ;
(
;
( ) element of
) element of
 is
the transition rate from state
is
the transition rate from state  to state
to state 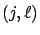 for
for  .
.
For example, in Figure 3.8(b),




Next: Markovian arrival process
Up: Quasi-birth-and-death process
Previous: Examples of QBD processes
Contents
Takayuki Osogami
2005-07-19
![]() , where the state space
can be divided into levels, and level
, where the state space
can be divided into levels, and level ![]() has
has ![]() states
(phases) for each
states
(phases) for each ![]() 3.2.
For example, in Figure 3.8(b),
3.2.
For example, in Figure 3.8(b), ![]() and
and ![]() for
for ![]() .
In a QBD process, transitions are allowed only
to the neighboring levels or within the same level.
Thus, a QBD process has a generator matrix of the form:
.
In a QBD process, transitions are allowed only
to the neighboring levels or within the same level.
Thus, a QBD process has a generator matrix of the form:
