



Next: Examples of GFB processes
Up: FB, RFB, and GFB
Previous: Preemptive priority queue
Contents
The GFB process is a generalization of the FB process, and is a 2D
Markov chain having less restrictions on its structure than the FB
process. Specifically, we allow the background and foreground process
to have complex interactions while the background process is in
levels  (and as a result, the GFB process behaves
like a QBD process when the background process is in levels
(and as a result, the GFB process behaves
like a QBD process when the background process is in levels
 ), but the GFB process behaves like an FB process when
the background process is in levels
), but the GFB process behaves like an FB process when
the background process is in levels  (see Figure 3.17).
Recall that, in the FB process, the background
process is a fixed QBD process, and only the behavior of the
foreground process is affected by the level of the background
process while the background process is in levels
(see Figure 3.17).
Recall that, in the FB process, the background
process is a fixed QBD process, and only the behavior of the
foreground process is affected by the level of the background
process while the background process is in levels  .
.
Figure 3.17:
The structure of the GFB process.
|
|
Essential restrictions in the GFB process are that
- There exists a level,
 , in the background process such that
each of the background and foreground processes is a fixed QBD process
while the background process is in levels
, in the background process such that
each of the background and foreground processes is a fixed QBD process
while the background process is in levels  .
.
- There is no transition from level
 to level
to level 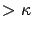 (i.e., any transition from level
(i.e., any transition from level  to level
to level  is to level
is to level  )
in the background process.
)
in the background process.
Given a 2D Markov chain, if one can identify the background and
foreground process that constitute the 2D Markov chain and that satisfy
the above restrictions, the 2D Markov chain can be reduced to a 1D
Markov chain via DR. However, the resulting 1D Markov chain may not
be analyzed efficiently. Thus, additionally, we require that
- Any transition in the 2D Markov chain changes the level of the foreground process by at most one.
If a 2D Markov chain satisfy the above two requirements,
the 2D Markov chain can be reduced to a 1D Markov chain via DR,
and the 1D Markov chain is a QBD process. We call such a 2D Markov chain
a GFB process.




Next: Examples of GFB processes
Up: FB, RFB, and GFB
Previous: Preemptive priority queue
Contents
Takayuki Osogami
2005-07-19
![]() (and as a result, the GFB process behaves
like a QBD process when the background process is in levels
(and as a result, the GFB process behaves
like a QBD process when the background process is in levels
![]() ), but the GFB process behaves like an FB process when
the background process is in levels
), but the GFB process behaves like an FB process when
the background process is in levels ![]() (see Figure 3.17).
Recall that, in the FB process, the background
process is a fixed QBD process, and only the behavior of the
foreground process is affected by the level of the background
process while the background process is in levels
(see Figure 3.17).
Recall that, in the FB process, the background
process is a fixed QBD process, and only the behavior of the
foreground process is affected by the level of the background
process while the background process is in levels ![]() .
.