Robot 3D view¶
The Robot 3D view displays, in a 3D representation, the current position of the joints of the robot you are connected to.

Performances: it is updated as soon as you move a joint, playing a behavior, or moving a joint manually (if it is a real robot) or through the motion widget.
Limitations: The torso of the robot is static. It is the reference of this 3D view. The limbs and the head of the robot moves around the torso which does not move. So even if your real robot falls over, you will not see it lied down in the 3D view. You will only see the position of its joints.
Changing the point of view¶
You can directly change the point of view by right-clicking on the 3D view and selecting the point of view you wish. By default, the point of view is on the front of the robot.
Moving joints¶
You can also select any moving part of the robot (head or limbs) by simply clicking on it. This action will open the Motion widget where you will be able to move the concerned joints.
Note
If you want to make your real robot move using the motion widget, you first need to stiffen the joints of your robot.
Selecting a different simulated robot¶
Moreover if you are connected to a simulated robot, you can change the model and the hardware version of the robot. To do so, go to the menu Edit > Preferences. In the tab NAOqi’s settings select the model and the hardware version corresponding to what you want. You should know that:
- V4.0, V3.3 and V3.2 correspond to NAO’s available hardware versions.
- H25, H21, T14 and T2 correspond to NAO’s available body type.
Motion widget¶
The Motion widget enables you to modify the joints values of each limb.

Here are the actions you can make using this widget:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| (1) | The slider enables you to adjust the joint value. You can easily move it, as well as enter a value in the associated text box. |
(2) 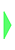

|
The little green arrow you can see at the bottom of the slider is the current joint value of the robot. Using the slider or text box will send a command to change the value of the joint. The robot will then try to reach the command value with its joint as soon as possible. If the arrow is blue, it means that the joint does not reach the command value you sent. When you send a new command, it usually takes one second or so for the robot to get to the right position. So if it takes longer, it means that the joint cannot reach the command value. It is the case when there is an obstacle as an other body part or a wall for instance. Note This slider has no effect as long as the concerned joint is not stiffened. You must first set the stiffness on using the Enslave chain on/off button to be able to change the joint value. |
(3) 


|
The record button enables you to save the defined value. This button can be:
For an example of use of this button, see the tutorial to create a movement on a real NAO. |
| (4) | The Mirroring option enables you to execute the same actions (send a command value, register a joint value, etc) on the symmetric limb as a mirror. For example if you select the right arm and enable this option, if you move the right shoulder, then the left shoulder will move the same way. |
(5) 


|
The Enslave chain on/off button enables you to set on/off the stiffness of the whole selected chain of joints of the robot. For example if you select the right arm and click on this button, all the joints of the right arm will be stiffened on or off. This button can be:
|
You will see the result of your actions on the 3D view and/or on your real robot (if connected to any).
To go further, an example of use of this Motion widget can be found in the tutorial Create a movement from scratch.